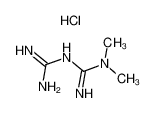
Metformin hydrochloride is a biguanide antihyperglycemic agent. Through glucose clamp investigation in rats 1,1-Dimethylbiguanide, Hydrochloride has been shown to lower blood glucose levels through improved glucose tolerance without stimulating insulin secretion, promoting weight gain or causing hypoglycemia. 1,1-Dimethylbiguanide, Hydrochloride reduces the diabetic complications on the cardiovascular system and increases insulin sensitivity. 1,1-Dimethylbiguanide, Hydrochloride has been shown not to change the synthesis of either GLUT4 or GLUT1 but does stimulate the transport of GLUT1 to the plasma membrane as seen in skeletal muscles. 1,1-Dimethylbiguanide, Hydrochloride has also been observed to improve peripheral arterials through selective reduction of PAI- 1 (plasminogen activator inhibitor). In Xenopus oocytes, 1,1-Dimethylbiguanide, Hydrochloride has been documented to act by increasing intercellular calcium concentration in addition to elevating receptor tyrosine kinase activity and inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate. 1,1-Dimethylbiguanide, Hydrochloride has demonstrated the ability to induce fatty acid oxidation and to stimulate AMP-activated protein kinase leading to the reduction in acetyl-CoA carboxylase activity. In brown adipocytes 1,1-Dimethylbiguanide, Hydrochloride has been observed to inhibit leptin secretion via a mitogen-activated protein kinase signalling pathway. |
 China
China